How to set up nRF5 SDK with ARM GCC¶
Introduction¶
The nRF5 SDK is your first stop for building fully featured, reliable and secure applications with the nRF52 and nRF51 Series. It offers developers a wealth of varied modules and examples right across the spectrum including numerous Bluetooth Low Energy profiles, Device Firmware Upgrade (DFU), GATT serializer and driver support for all peripherals on all nRF5 Series devices. The nRF5 SDK will almost certainly have something for your needs in developing exciting yet robust wireless products.
The SDK is delivered as a plain .zip-archive, which makes it easy to install as well as giving you the freedom to choose the IDE and compiler of your choice.
Here we will describe how to set up the nRF5 SDK development environment on your system, build and run the example applications.
Install GNU Arm Embedded Toolchain¶
The GNU Embedded Toolchain for Arm is a ready-to-use, open source suite of tools for C, C++ and Assembly programming targeting Arm Cortex-M and Cortex-R family of processors. It includes the GNU Compiler (GCC) and is available free of charge directly from Arm for embedded software development on Windows, Linux and macOS operating systems.
Download and install the GNU ARM Embedded Toolchain. The 6-2017-q2-update version is recommended. Then ensure the path is added to your OS PATH environment variable.
# in ~/.bash_profile, add the following script
export PATH="<path to install directory>/gcc-arm-none-eabi-6-2017-q2-update/bin:${PATH}"
Type the following in your terminal to verify if the path is set correctly:
Install GNU make¶
Now with the toolchain installed we can build object files from source code, but to build projects based on makefiles, which can be seen as a recipes for the builds, we need to have GNU make installed on the system.
On Windows the easiest way to install the dependencies is to use the MSYS2. You can do so by performing the following steps:
-
Download and run the installer - "x86_64" for 64-bit, "i686" for 32-bit Windows.
-
Update the package database and core system packages with:
-
If needed, close MSYS2, run it again from Start menu. Update the rest with:
-
Install make:
GNU make is bundled with Xcode tools if working on macOS. On Linux it may be different ways to obtain GNU make depending on your distro, if not installed already, e.g. on Ubuntu you can get by entering this command:
Clone the repository¶
Clone the nRF52840-MDK repository from GitHub:
Install the nRF5 SDK¶
Download the SDK file nRF5_SDK_v15.2.0_9412b96 from https://www.nordicsemi.com . Note that the current version is 15.2.0.
Extract the zip file to the nrf52840-mdk/nrf_sdks directory. This should give you the following folder structure:
./nrf52840-mdk/
├── LICENSE
├── README.md
├── firmware
├── config
├── docs
├── examples
├── mkdocs.yml
├── nrf_sdks
│ └── nRF5_SDK_v15.2.0_9412b96
└── tools
To build an example application you first need to set the toolchain path in makefile.windows or makefile.posix depending on platform you are using. That is, the .posix should be edited if your are working on either Linux or macOS. These files are located in:
Open the file in a text editor, and make sure that the GNU_INSTALL_ROOT variable is pointing to your GNU Arm Embedded Toolchain install directory.
GNU_INSTALL_ROOT ?= $(HOME)/gcc-arm-none-eabi/gcc-arm-none-eabi-6-2017-q2-update/bin/
GNU_VERSION ?= 6.3.1
GNU_PREFIX ?= arm-none-eabi
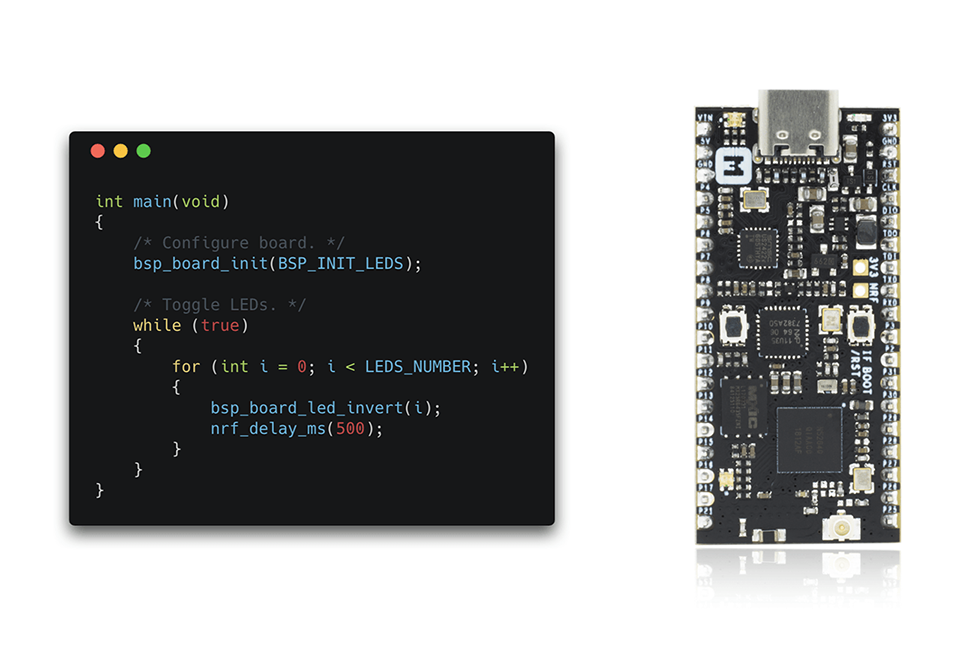
Build and run the blinky example¶
Now you can try to build one of the examples. Will use the blinky example here to keep it simple.
Open terminal and change directory to:
Connect the nRF52840-MDK to one of your PC's USB host ports. Compile and program the example:
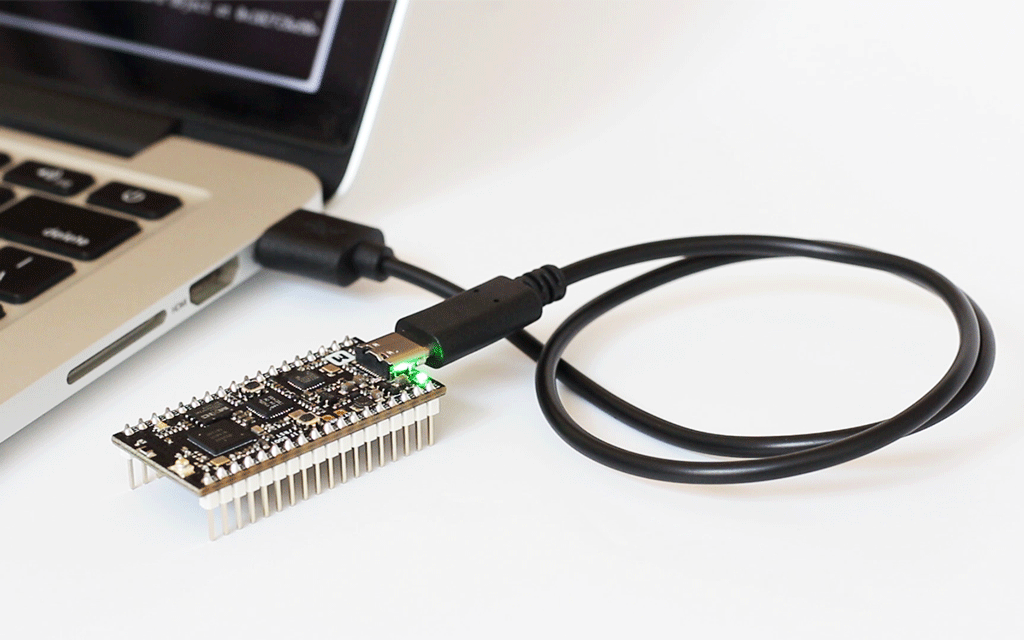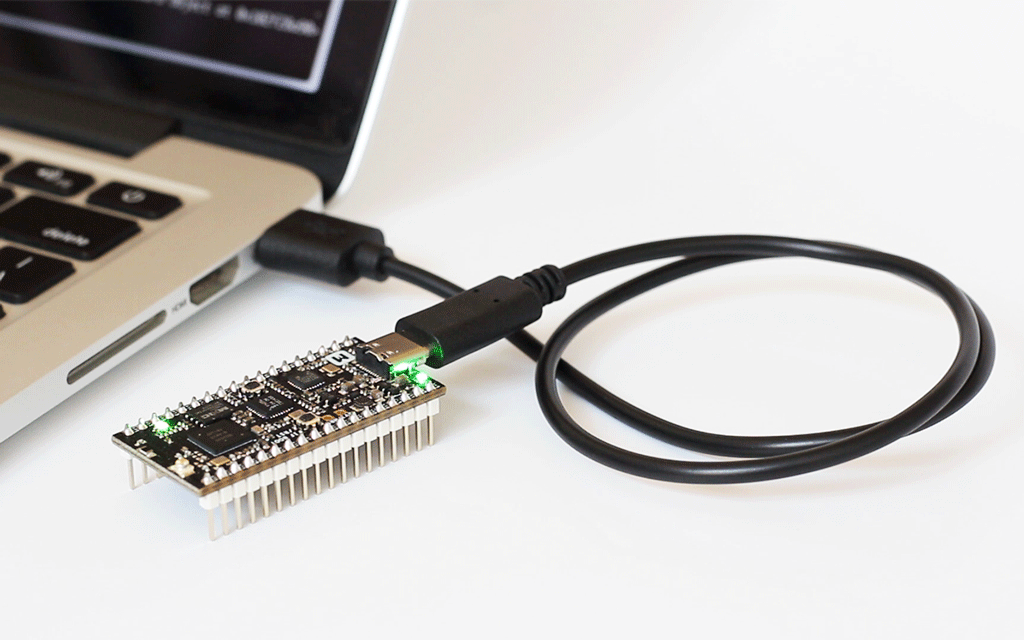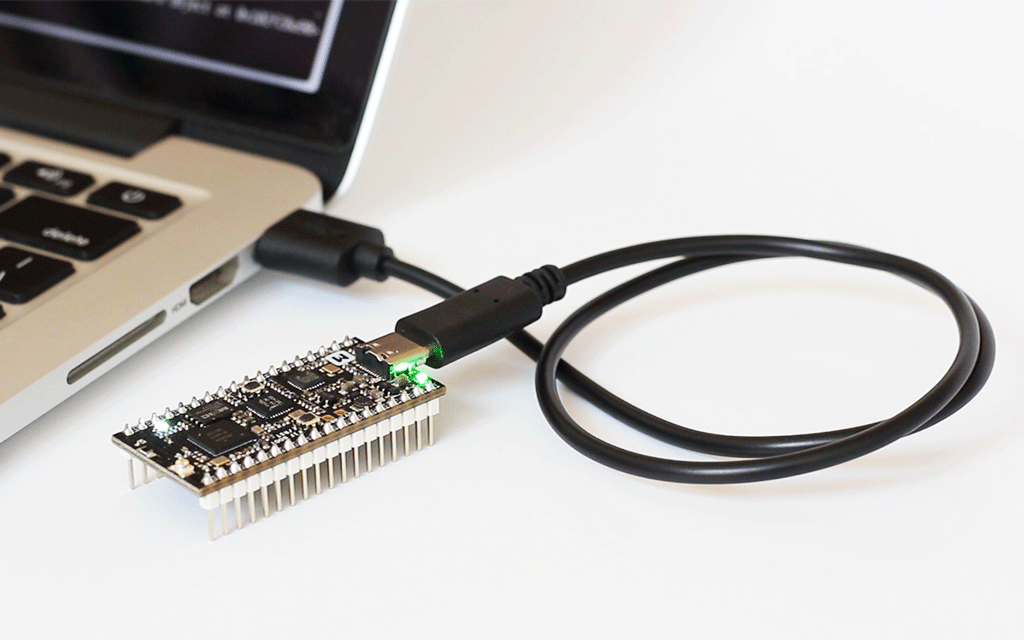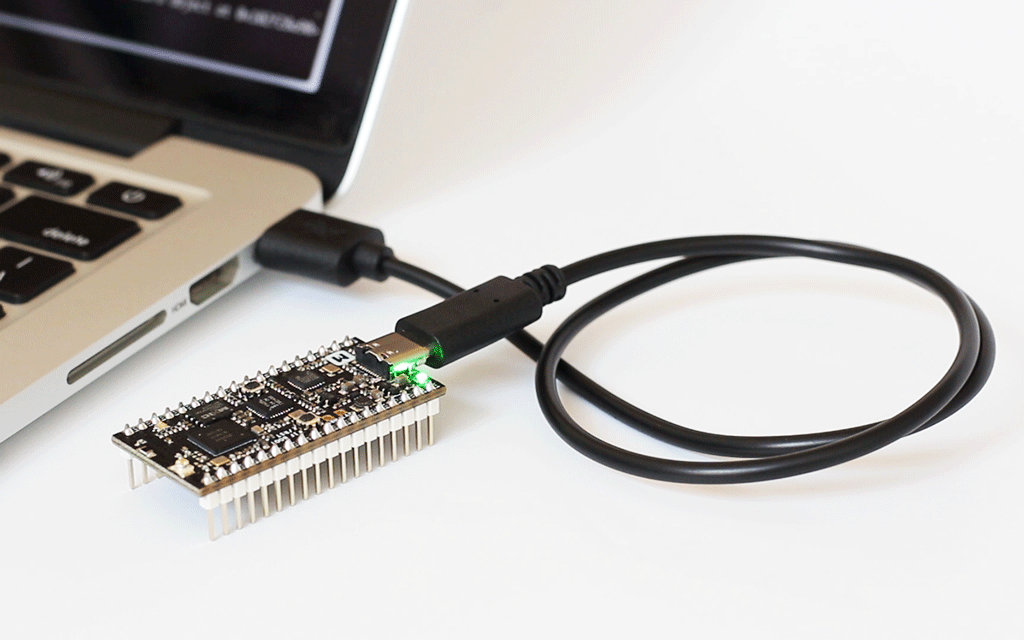
Run examples with SoftDevice¶
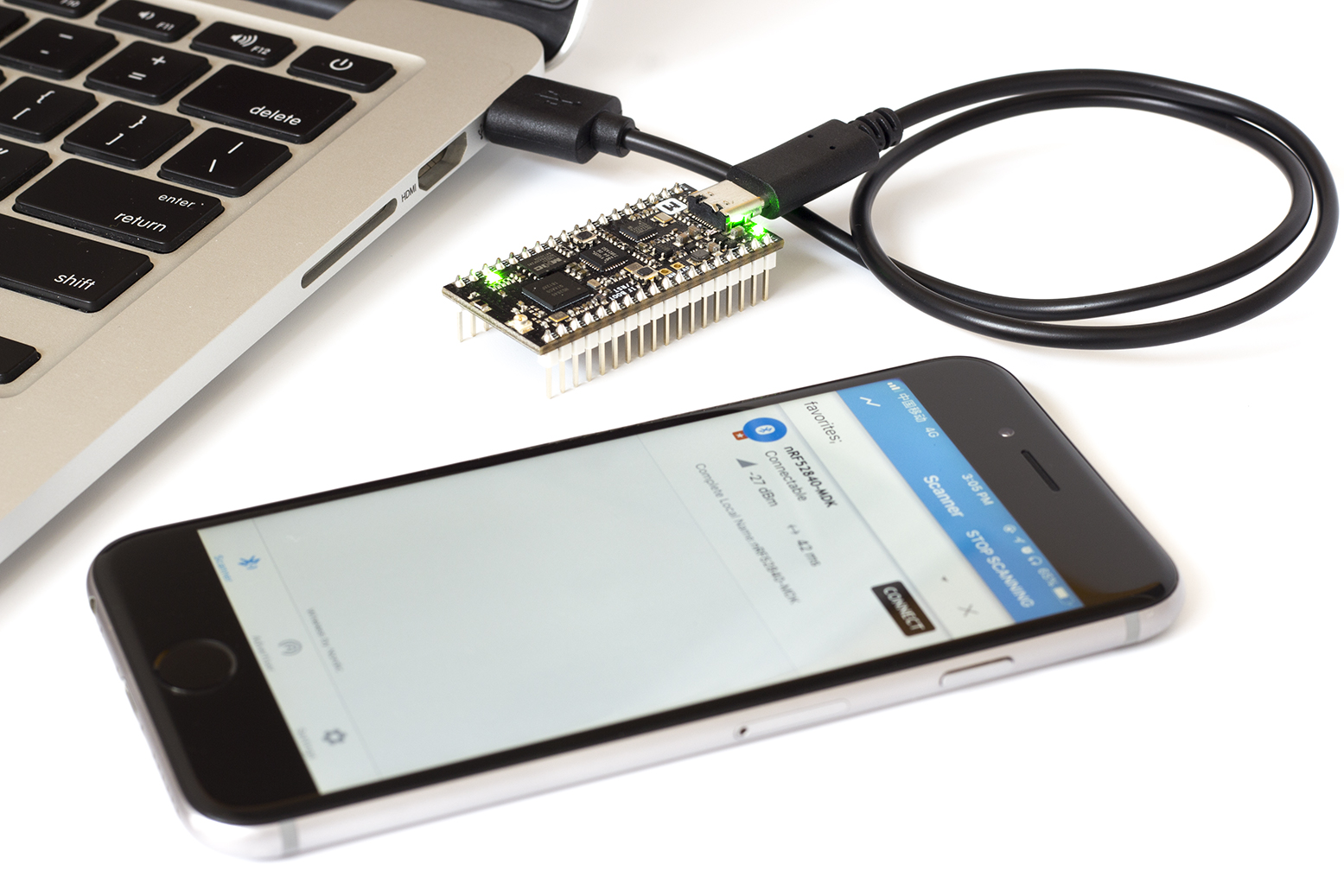
Before you can run more advanced examples that use Bluetooth or ANT, you must program the SoftDevice on the board.
The SoftDevice binary is located in folder components/softdevice/<Softdevice>/hex in the SDK, where <Softdevice> is the name of the SoftDevice.
The easiest way to program the SoftDevice is using the GCC makefile of an example:
-
Open a command prompt in the folder that contains the makefile of an example. The example must require a SoftDevice. For example, the
ble_app_blinkyexample. -
Run the following command:

More examples¶
Over time, more example applications will be added to the repository. You can star or watch the nrf52840-mdk repository to stay up to date.
